What is EDI in Logistics?
What is EDI?
EDI or Electronic Data Interchange is a system that lets two different networks connect with the purpose of exchanging data electronically. This is an inter-organizational system that facilitates the computer-to-computer exchange of data between multiple business systems. This process overall eliminated the need for paper, saving business time and money when conducting business with trading partners. Additionally, EDI is much more efficient as it takes much less time to manage trading partners in your business as well as keeps everything extremely organized in its data system.
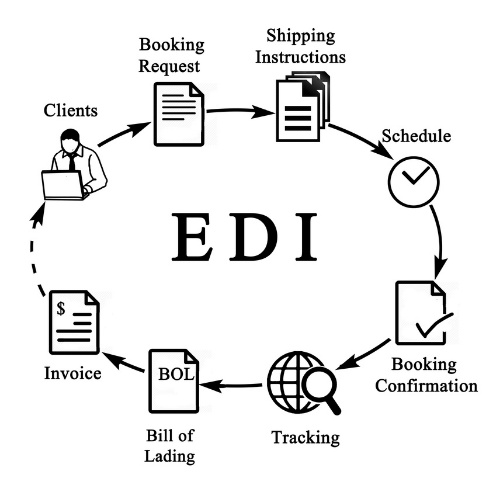
How Does EDI Work?
Electronic Data Interchange is the exchange or transfer of data between systems with the purpose of processing goods or shipments, and for additional financial tasks. This process saves time as it automatically processes the information stored in the system, and knows how to transfer the data based on your specifications. This eliminates the need for individuals to manually enter data for every shipment of invoice their business receives.
Although the basic concept of EDI stays the same throughout every concrete definition, there are different ways EDI can be seen in logistics based on what exactly you are using it for:
Computer-Computer EDI:
In computer to computer electronic data interchange, the need for physical mail, fax, and email is replaced. Even though email is technically still electronic, people still have to manage them in some way. Computer to computer EDI completely eliminates the need for people to be involved. It greatly speeds up the process of managing these documents and creates a more effective and productive environment for all businesses involved. Additionally, computer to computer EDI removes the possibility of human error, as humans are not involved in the exchange of documents and information.
Standard Format EDI:
Standard format is what each computer needs to be equipped with in order to understand and process such documents. As humans are not involved in EDI, this standard format ensures that computers will read and sort documents properly. Typically, the standard format looks at information such as day/month/year or any numbers involved in a document. Without this format, companies that use different technical languages or an international language wouldn't be properly understood by EDI. These numbers eliminate the need for language to be as involved, and for computers around the world to understand different documents.
Business Documents EDI:
Through EDI, there are many different types of documents exchanged through businesses. Some of these documents include purchase orders, ship notices, and invoices. In this case, EDI reads, sorts, and exchanges necessary documents.
What are the Advantages of EDI?
Businesses decide to use electronic data interchange for many reasons to help improve their company. Below are some reasons why businesses may utilize EDI:
Automate Processes:
As EDI is all electronic, it eliminates the need for both human intervention and the possibility of human error. This lets businesses focus on other aspects of their company without having to increase their workload and focus on inputting and keeping track of data.
Increase Customer Satisfaction:
EDI increases delivery speeds and keeps track of all things logistics. Customers and businesses alike can count on real-life updates of tracking, shipping, and receiving notices through EDI. As customer satisfaction increases, so does customer retention.
Improve Data Exchange:
Typically, logistic companies are overhead worth the amount of data they have to keep track of in a distribution channel. EDI automatically handles all things data exchange between the companies in a distribution channel. This creates easy and effective data exchange between companies, and therefore faster processing and delivery of products.
Eliminates Paperwork:
As EDI is electronic, the need for all paperwork is no longer needed. In logistic companies, there can be endless forms of paperwork such as packing slips, order forms, delivery notes, etc. In EDI, all of this is exchanged electronically, keeping your business much more organized and functional.
What are the Disadvantages of EDI?
Although there are many advantages to implementing EDI in your business, you should also consider common aspects companies find disadvantageous:
The Cost:
Although EDI can eliminate costs in the future for your businesses, it is quite expensive to set up within a company. Smaller businesses especially find it difficult to redesign their current applications to fit EDI standards. You should be prepared for the initial setup of EDI in your business to be expensive and time-consuming.
Standards to Maintain:
If you are looking into setting up EDI for your business, you should be aware of the standards involved. Certain standards in EDI make it difficult or impossible for smaller businesses to communicate or exchange information with larger ones. As different editions to document standards are updated, smaller companies might not be able to keep up as much with maintaining standards, making it difficult to use EDI with other companies.
Maintenance and Backup System:
Once EDI is set up for your business, it then becomes what that company relies on. This means there needs to be routine maintenance on the system to ensure it is running smoothly. Additionally, there needs to be some backup system in place just in case your EDI system fails. Both require attentive maintenance.
Is EDI Right For Your Business?
Overall, there are many advantages to implementing EDI in your business. It can alleviate some of the stress of managing all the data involved with business exchanges or distribution channels. Additionally, EDI keeps everything organized and up to date. This makes things in your company run smoother and more effectively. Setting up EDI in your business may be costly and time-consuming, but if the advantages outweigh those two factors, EDI might be a great choice for your company.